Analysis of the fast food market in Kazakhstan
Abstract
The role of LSM (local store marketing) in the development of the fast food market is very important. It is a marketing service that can be used to properly manage communications, demonstrate the effectiveness of advertising and as the basis for promotion and stock mechanics. Nowadays, the fast food market in Kazakhstan is worth around 280-310 million. Despite the economic situation, the fast food market continues its dynamic development. The market has a capacity of about 280-310 million. The biggest players are Burger King and KFC. LSM plays a crucial role in the fast food market. There should be plenty of places to sell since this is a fast food service. An individual marketing and development plan should be developed and implemented for each restaurant. There are more than 29 Burger King Restaurants in Kazakhstan, and each restaurant should create communication based on location. It was revealed that the fast food market in Kazakhstan is not sufficiently developed in comparison with foreign markets, and ways to solve this problem were considered. Comparisons have been made with Western Europe, the USA and Asia countries. The author makes a conclusion that intensive development of the fast food chain is required.
Keywords: fast food service market, local store marketing (LSM), restaurant, food, catering, Fast Food, marketing tools
Introduction. LSM takes restaurants to a new level of the fast food market. However, it is negatively affected by underdeveloped market and the occurrence of many unexpected problems. The reason for choosing this topic is the achievement of high-quality communications in the market by developing LSM. It can also affect the creation of new jobs in the market and the transfer of the one to a new level of technology by increasing the quality of the offer (Avrutskaya, Tarabrina, 2018).
The aim of the work is the development of recommendations for improving local marketing services in the fast food market.
Materials and Methods. The article uses methods of marketing research of the fast food market, consumer surveys and statistical data analysis.
Results and Discussion. Catering is one of the sectors of the economy that produces and supplies food products to a specific group of the population (Kuzembayev, Kuzembayeva and Smagulova, 2013).
There are several types of catering depending on the specifics of the service, assortment and features of the culinary products.
Let’s consider catering in terms of “Industrial trade” characteristics:
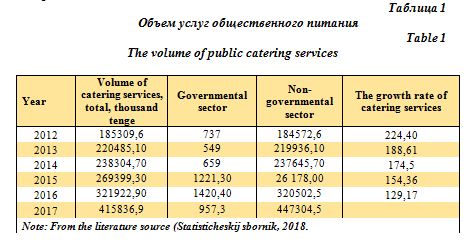
By looking at the statistics, the dynamics of growth in the volume of catering services can be observed (Table 1) (Statisticheskij sbornik, 2018).
Table 1 illustrates the volume of catering services for 2012-2017. The volume of public catering services in the state and non-governmental sectors and their growth rates are also indicated. It increased by 2.2 times in 2017 compared with 2012, and 88.61% in comparison with 2013. The volume has grown by 74.5%, if compared with 2014. Moreover, it shows an increase of 29.17% in comparison with 2016.
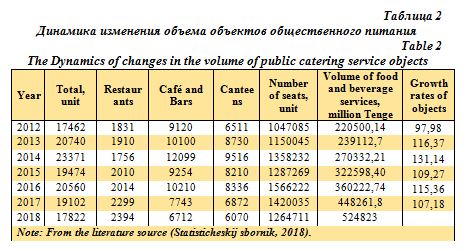
The table below shows the dynamics of changes in the volume of dining rooms, cafes, restaurants and bars.
The development of technology has expanded the variety of products and accelerated the speed of service. In this regard, the number of fast food service companies or the "fast food" restaurants as often use nowadays has increased. In this article, one of the sector of public catering fast food chains were reviewed.
Regarding the history of fast food enterprises, one common mistake today is the conclusion that fast food businesses appeared in the 20th century. In general, fast food service appeared in ancient Rome. In addition, an analogue of fast food called Bistro opened in Paris in 1814.
Currently, there are many fast food chains in the world. Let's look at the examples:
- burger – McDonald`s, Burger King;
- pizza – Pizza Hut;
- seafood – Red Lobster;
- chicken foods – KFC;
- beef steak – Sizzler;
- sandwich – Subway;
- pancake – Country Kitchen (Kotler, Bowen and Makens, 2007).
The main leaders of the fast-food chain in the Republic of Kazakhstan are:
- Burger King;
- KFC;
- Hardee`s;
- MCDonald`s.
The Kazakhstan's fast-food market is under development. The KFC fast food chain, which first entered the Kazakhstan fast food market in 2010, is a leader among others. Nowadays, the KFC chain has opened 34 restaurants in five cities of Kazakhstan (Almaty, Nur-Sultan, Karaganda, Pavlodar, Shymkent). In 2011, Hardee`s restaurants joined the Kazakhstan fast food market. Hardee's currently has 13 restaurants in Almaty, Nur-Sultan and Karaganda cities. Burger King Chain entered the market in 2012 and today operates 29 restaurants in Almaty, Nur-Sultan, Aktau, Atyrau, Aktobe, Karaganda, Uralsk and Pavlodar. On February 15, 2016, a new player McDonald's entered the market. There are currently five restaurants in Almaty and Nur-Sultan (Statisticheskaja informacija agentstva «Good», 2020).
According to Burger King Kazakhstan, the annual turnover of the Kazakhstan's fast food market is about $ 245-260 million. The annual market growth is expected to reach 10-12% in the opinion of company experts (McCANN Creative Agency, 2020).
20% of Almaty residents aged 18 to 35 visit fast food restaurants once a week, and 25-30% of people eat fast food twice a week based on Burger King figures. From the above age group, 47.4% of Kazakhstanis prefer to spend time in cafes and bars.
Using the Mystery shopping method, also relying on the 230 people survey results, we came to the following facts (About “Burgerking” Company, 2020):
Every customer under the age of 40 eats fast food once a year in Almaty.
Over 54% of the population eat hamburgers per month;
An average of 25-30 hamburgers are served to the guest of the target audience;
The important points of fast food restaurants are cleanliness (91%), reasonable prices (69%) and places for guests (63%).
According to the survey “Why do you like fast food?”, it was established that almost half of the population (46% of people) buy fast food because of the taste. In the modern world, people are busy and often have no time for eating. Therefore convenience (26%), the posibility to eat on the go (11%) and fast-food fullness (5%) attract busy people. As for the prices, the average hamburger costs 450 tenge, which is an affordable price (9%), and some may even be cheaper (3%).
To the question "Why people do not like fast food?" more than half of the population (58%) replied that fast food is very harmful. Fast food contains many calories for some people (18%). Some respondents (9%) noted a high market price for food. There is also an opinion that fast food is not convenient for everyone (6%) and that discomfort leads to poor quality (5%).
What is fast food service marketing? Marketing is not only promotion for sale or through advertising; it has a deep meaning. Nevertheless, its main goal is to increase sales. However, an extensive marketing system does not always meet the needs of private restaurants (Mill, 2009). For example, some restaurants may suffer from very low sales from Monday to Friday, while others may have higher sales on weekends. Therefore, local marketing or LSM must be developed to fill such gaps in the marketing system. Local restaurant marketing is a disciplined marketing process for the restaurant clients who are nearby. The keyword is “Discipline”, because it is limited in time and money. So it is important that the marketing efforts are focused on good results.
LSM is the local marketing of a particular restaurant in this case. To explain in more detail, it is a combination of marketing activities or services that helps the restaurant interact with the local community and guests (consumers). Three key variables are considered in LSM: consumer, competition, and restaurant characteristic (Yesenalina, 2016).
The main advantage of this tool is that the process of attracting the customers is carried out at the local level. This means at the restaurant level, so customer relations and communication will be at a high level. Potential customers are calculated based on the restaurant location or, if the client is in a radius of 1.6-8 km, he/she is a potential client for LSM.
Local restaurant marketing requires many types of communication. These include BTL outdoor advertising, promoters’ services, Stella, Roll, Showbiz, Tale, banner and others. The marketing activities of local restaurants involve a particular restaurant, its promotion and development (“What is Local Store Marketing?”).
Each restaurant has its own Trade Area. It is divided into two types: for pedestrians and transport users (Nordfalt, 2015).
Pedestrian trade area is calculated in meters. The smallest and most important area is Zone A, the diameter of Zone A trade area is 120 meters, and the restaurant is within1-2 minutes walking distance. Zone B is within 240 meters, and the restaurant is 2-4 minutes away. Zone C is 320 meters , the time range is 4-6 minutes. Last, the largest zone D is 520 meters; it takes 6-10 minutes to get to the restaurant.
The next important step is to find places where consumer traffic is generated. Such places are entertainment centers, stadiums, theaters, cinemas, parks and other recreation zones (Kak konvertirovat' veb-trafik v zhivyh klientov restorana, 2019). It is necessary to find target audience among them and direct the communication channels to this traffic collector. Generally, Burger King customers are between 16-35 years old. In this regard, there is a need to direct communication tools towards the demographic segment at the age of 16 to 35 years.
As for the production and structural processes of outdoor advertising, there are many types and structures of outdoor advertising. The main of them are discounts related to promotions, new products and certain products. The frequency of advertising campaign updates is 2 months for the international brand Burger King. The frequency of new products release is about three months. Consequently, the frequency of change of local restaurant communications is also from two to three months. Any advertising action or implementation of a new product should be distributed throughout Kazakhstan. Therefore, operational processes are highly important and directly depend on factors such as time and logistics. Each promo has its own post material, they also change in each promo (8 shagov k uspeshnomu planirovaniju prodvizhenija restorana, 2014). The post materials include:
- Menu at the checkout, 3-5 items;
- Info board post materials;
- Roll ups, an average about 3 items;
- Tray liners;
- Visuals are developed for each promo and they change on cash monitors and the board menu.
- Banners on the windows and walls of the restaurant, about 3 items.
Television advertising is used to reach the audience that is a passive Internet user. In particular, advertising banners are shown on GAKKU, Muzzone, 31, Hit TV and NTK channels during a weather forecast transmission.
The structure of LSM materials primarily relates to the goods sold. The process of choosing a product that should increase sales or promotion is based on low sales, new or target audiences. The next step is calculation of the cost, analysis of traffic generators and sales sources. As a result of this process, the designer and the marketing department must develop a general LSM material. The following step is posting the visual after its readiness. After all the material is be prepared, it is delivered to the media and advertising agencies. Outsourcing services in this process include the posting, movement and processing of communication materials (Sistema lokal'nogo marketinga v restorane, 2019).
Nowadays, there are 29 restaurants of the Burger King Chain in Kazakhstan. If to consider the fact that advertising campaign changes at a two-month interval and a new product at three-month interval, the total LSM expenses can be evaluated, calculated and analyzed. In total, the campaign should be held 6-7 times a year, a new product should fill the assortment menu with 3-4 items. Based on these figures, 29 restaurants need a large amount of LSM communication materials. The changes affect not only the outside of the restaurant, but also LSM materials inside. Menus, roll ups, window and wall communications are changing. In the case of developing the above described LSM material, it can be seen that the LSM material changes very often and the cost is very high (Tarabrina, 2018).
Some types of communications for customers – car users – are different. These include banners, stellas, navigation advertisements, radio tones and stop banners. The only thing that does not apply to LSM is the radio, so it won’t be considered. Some forms of communication are general to pedestrian customers and car users for a local restaurant. These are banners, intermediate advertising, steles and tray liners. The mechanism for calculating the trade area of consumers – car users – is calculated differently. The distance of 10 minutes drive away by car 60 kilometers per hour from the restaurant to east, west, north and south side will be calculated. Moreover, such factors as traffic light waiting time, pedestrian waiting time and traffic jams should be taken into consideration.
LSM materials for each restaurant are created on the basis of the Trade Area. The navigation communications are often used for car consumers.
Conclusions.Currently, the dynamics of public catering is growing. As can be seen from the statistics, the number of services provided has increased by 119%, or the number of public catering enterprises has increased by 105.6%.
In general, the fast food market in Kazakhstan has a stereotypical concept about “fast food” as a harmful food product. However, fast food has found its regular customers, and there is no doubt that its expansion will continue.
Market expansion stimulates to seek new communications. It is known that the emergence of new subgroups in a new consumer segment with market expansion is additional revenue for each company. It needs to build the proper communication to solve the problem of attracting these customers. However, considering each element of communication separately, it is impossible to achieve a result. Accordingly, it is necessary to have a well-designed mechanism. Planning and developing mechanisms from beginning to end is the LSM's core work. LSM deals with the entire chain, from consumers to competitors, not only with communications.
Conflicts of Interest: the authors have no conflict of interests to declare.




















Reference lists
“About “Burgerking” Company”, [Online], available at: https://burgerking.kz/ru/about (Accessed 14.01.2020).
“Kak konvertirovat' veb-trafik v zhivyh klientov restorana”, (2019), [Online], available at: https://pear-group.ru/kak-konvertirovat-veb-trafik-v-zhivyx-klientov-restorana/ (Accessed 14.01.2020).
“Roznichnaja i optovaja torgovlja v Respublike Kazahstan”, (2018), Statisticheskij sbornik [Electronic], Astana, Kazakhstan, pp. 96-97, available at: https://stat.gov.kz/official/industry/17/publication (Accessed 10.01.2020).
“Sistema lokal'nogo marketinga v restorane”, (2019), [Online], available at: https://vc.ru/marketing/55670-sistema-lokalnogo-marketinga-v-restorane (Accessed 20.01.2020).
“Statisticheskaja informacija agentstva «Good», rabotajushhego v sfere strategicheskogo konsaltinga”, [Online], available at: http://good.kz (Accessed 12.01.2020).
“What is Local Store Marketing?”, [Online], available at: https://lsmguide.com/what-is-local-store-marketing/ (Accessed 14.01.2020)
Avrutskaya, I.G. and Tarabrina, O.A. (2018), 120 instrumentov lokal'nogo marketinga. Srazhenie na svoej territorii [120 local marketing tools. Battle on its territory], Restaurant statements, Moscow, Russia.
Kotler, Ph., Bowen, J.T. and Makens, J. (2007), Marketing. Gostepriimstvo. Turizm [Marketing. Hospitality. Tourism], Juniti-Dana, Moscow, Russia.
Kuzembayev, K., Kuzembayeva, G.K. and Smagulova, A.K. (2013), Kogamdyk tamaktandyru ondіrіsіn ujymdastyru [Public Catering organization], Almaty Technological University, Almaty, Kazakhstan.
McCANN Creative Agency, [Online], available at: https://mccann.kz/ (Accessed 12.01.2020).
Mill, R.Ch. (2009), Upravlenie restoranom [Restaurant Management], Juniti-Dana, Moscow, Russia.
Nordfalt, J. (2015), Ritejl-marketing. Praktiki i issledovanija [Retail marketing. Practice and research], Translated by Yevstegneeva, I., Al'pina Publisher, Moscow, Russia.
Tarabrina, O. (2018), “ Kak privlech' gostej s pomoshh'ju instrumentov lokal'nogo marketinga” [Online], available at: http://restoranoff.ru/solutions/marketing/kak-privlech-gostey-s-pomoshchyu-instrumentov-lokalnogo-marketinga/ (Accessed 22.01.2020).
Yesenalina, A. (2016), “Rynok fastfuda Kazahstana ocenili v $260 mln” [Online], available at: https://lsm.kz/rynok-fastfuda-kazahstana-ocenili-v-260-mln (Accessed 14.01.2020).
“8 shagov k uspeshnomu planirovaniju prodvizhenija restorana ”, (2014), [Online], available at: http://prohotelia.com/2014/12/successful-restaurant-promotion-plan/ (Accessed 16.01.2020).