STRATEGIC PLANNING IN THE CONTEXT OF SUSTAINABLE TOURISM DEVELOPMENT
Abstract
The article presents some results of researches in the sphere of strategic planning in the context of sustainable tourism development management. The authors performed an analysis of the present theory and methodology of strategic planning as a special function of tourism development management. The obtained results are logically sorted according to the following main directions: conceptual and normative foundations of strategic planning for sustainable tourism development; materials about the theory and methodology of strategic planning for sustainable tourism development; the principles and procedures of strategic planning for sustainable tourism development
Keywords: Sustainable tourism, strategic planning, scientific bases, development, management, Kazakhstan
Introduction. In general, the plan is a complex and differentiated model of the future condition of the recreation and tourism sphere on the specific territory. Planning is a continuous process of search of funding aimed at the distribution of resources for achieving the terms and sequence of management character. The main tasks of planning are the following: ensuring purposeful development; coordination of activity for all interested subjects; creation of the infrastructure of effective assessment, control and monitoring; motivation and encouragement of activity of all interested subjects; information support, marketing and branding.
Strategic planning is a special function of tourism sustainable development management in the long term. Works of many experts dealing with management issues in tourism are devoted to this problem. Among them: Filip Kotler (over 100 monographs and articles on strategic marketing), Robert Braymer («Bases of management in the industry of hospitality», 1995), John Walker («Introduction to hospitality», 2013), Alexey Danilovich Chudnovsky («Tourism and hotel economy», 2005), Galina Alekseevna Karpova («Economy of modern tourism», 1998), etc. The American expert in the field of tourism planning Edward Inskeep in the book «Tourism Planning: An Integrated and Sustainable Development Approach» (1st Edition from 1991) suggests to consider strategic planning as the organization of the future for achievement of an accurately definite purposes and tasks number. In the course of strategic planning necessary balance between production and consumption of tourist products and services, volume of market demand for them and volumes of their production is provided [1, 2, 3].
France, Great Britain and Canada were the strategic planning pioneers in tourism in the early 1960s. At the present stage, obtaining an environmentally sound, economically efficient and socially significant contribution of tourism is impossible without the concepts of sustainable development and green economy. In 2011, UNEP (United Nations Environment Programme) published a report «Towards «a green» economy: Pathways to Sustainable Development and Poverty Eradication». It presents a chapter «Investment in energy and resource efficiency: Tourism», written in collaboration with UNWTO. UNEP and UNWTO in 2012 published a document entitled «Tourism in the green economy: informational report» («Tourism in the green economy – background report»). UNWTO in 2013 prepared «The Guidelines for Sustainable Tourism Development – increasing opportunities for sustainable tourism development in developing countries» («Sustainable tourism for development guidebook – enhancing capacities for sustainable tourism for development in developing countries»). All of the work an important methodological basis for strategic planning in the management of sustainable tourism development.
Purpose of researches – the analysis of current theory and methodology of strategic planning as a special management development of sustainable tourism. It updates the following main areas of research:
a) to identify the conceptual and normative foundations of strategic planning for sustainable tourism development;
b) to compile material on the theory and methodology of strategic planning for sustainable tourism development;
c) to define the principles and procedures of strategic planning for sustainable tourism development.
Methods of researches. The studies are based on general scientific and special methods that take into account the specifics of the problem. Among the scientific methods we used: system, analysis, synthesis, evaluation of historical comparison, generalization, abstraction (except for non-essential information), and extrapolation of results. The private methods include: logical-formal, target-oriented and computer information processing technology. As the initial information we used some scientific publications on the issue and some planning strategies for sustainable tourism.
Research results and discussion. Strategic planning in a general view is a set of actions and decisions which lead to development of the specific strategy focused on achievement of a long-term goal of tourism development. In more detail strategic planning can be characterized as a process in which the logical analysis of current situation and future opportunities provide a formulation of a complex of long-term intentions, strategies, goals, and activities, taking into account possible chances and risks. Fig. 1 demonstrates three key components of strategic planning in tourism.

Fig. 1. Key components of strategic planning as a management special function for sustainable tourism development
Ключевые компоненты стратегического планирования как особой функции управления развитием устойчивого туризма
Strategic planning in tourism from a position of technology of performance can be defined as:
1) an iterative process including definition of mechanisms of achievement of a long-term goal, tasks and the expected results;
2) a multi-stage process of development of strategy for achievement of the results delivered to a long-term goal, tasks and the expected results;
3) a multipurpose process of distribution of the resources necessary for achievement of a long-term goal, tasks and the expected results.
In a general view strategic planning in tourism includes the following activities:
- analysis of potential, competitiveness and efficiency of use of a certain territory (market, direct and indirect competitors, demand, suppliers, types of products and services, other conditions and factors);
- formulation of the purpose of development of tourism on a certain territory for governing bodies, objects and subjects of the sphere of recreation and tourism;
- identification of tasks and mechanisms, determination of stages of the tourism sustainable development;
- identification of the expected results and indicators of the tourism sustainable development;
- development of a framework of actions of the tourism sustainable development.
Strategic planning in tourism begins with the development of a conceptual framework (scheme) of long-term support of sustainable development from a position of determination of competitiveness and developing a tourist image of the concrete territory of recreational and tourist designation. For this purpose they consider the following key characteristics: a geopolitical, ecological and tourist image; the culture of hospitality of the local population; a variety of opportunities for the organization of rest and tourism; the level of development of transport and other infrastructure; the quality of services; the compliance of quality of services with the price, etc. Each characteristic is estimated according to the system of indicators presented in comparable units of measure. Such units of measure can be the following: points, percent, unit shares (for example, 0,1 or 0,5 or 0,8), monetary indicators, power indicators (for example, 1 W = 0,62 USD), etс. The system of indicators clearly demonstrates advantages and disadvantages of the territory of recreational and tourist designation. It acts as a basis for the development of a long-term strategy of the tourism sustainable development. It gives information on all essentially important components of the tourism sustainable development (fig. 2).

Fig. 2. Main results pyramid of the strategic planning for sustainable tourism development
Пирамида главных результатов стратегического планирования развития устойчивого туризма
Under present conditions, it is expedient for strategic planning to subdivide the territory of all recreational and tourism destination into four main categories:
- an area with the most valuable and diverse conditions and resources that can be used for the development of both public recreation during holidays and special forms of tourism;
- the areas with various conditions and resources for short-term and seasonal tourism and recreation;
- the areas with limited resources, based on which recreation and tourism will be developed according to the needs of the local population and visitors in the organization of places for recreation and tourism;
- the territory with limited resources or no resources on which recreation and tourism will be developed on the initiative of local authorities as an alternative to the main directions of economic development.
Strategic planning of development of new territories for the tourism sustainable development should be based on the following provisions:
- scientific approach and sound policy;
- compulsory consideration of views and traditions of local communities;
- rational use of natural resources and values;
- flexible philosophy of territories development as a guarantor of balanced development;
- planned and systematic development of tourism;
- securing safety of tourists and tourism;
- optimal price-quality ratio of tourism products and services.
General orientation (the idea) defines the basic strategic planning model for sustainable tourism development (tab. 1).
Table 1
The basic model of sustainable tourism development strategy
Базовые модели стратегии развития устойчивого туризма

The following special tools of strategic planning for sustainable tourism development should be noted here: forecasting; design; programming.
A. The strategic prognosis uses both the experience gained in the past and current trends to determine the future. The result is a picture of the future, which can be used for planning. The purpose of forecasting – to receive evidence-based options for development trends (changes) of a managed object (indicators) in time and space. Sources of information for forecasts – verbal and written texts produced in the process of communication between people or from the media.
B. The strategic planning is a set of actions that contribute to sustainable tourism. The main aim is to take into account all the achievements of science and practice in the field of rational allocation of resources (labor, raw materials, technology, financial and other) and the influence of the environment and to ensure optimal coordination of the internal environment and the right to determine the activity in the future.
C. The strategic programming is based on the forecast (or Foresight) and is focused on the preparation of complex algorithms for solving the main problems of sustainable tourism (cross-industry, sectoral, regional, local). Algorithms actions typically comprise: 1) a list of key tasks; 2) the collection and sequence of events; 3) the calculation of direct and indirect (related) costs according to the main types of resources used; 4) the distribution of tasks in accordance with the terms and performers.
We will briefly consider the content and ratio of strategic, tactical and operational planning for development of sustainable tourism (fig. 3).
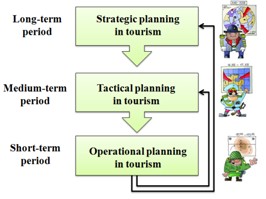
Fig. 3. The structure of planning for sustainable tourism development
Структура планирования для развития устойчивого туризма
The most important features of strategic planning for sustainable tourism development are the following:
- it plays the role of an impartial (independent) arrangement of territory management;
- it considers alternatives to a broad range of areas;
- it is characterized by the uncertainty and importance of studying the risks of development of the territory;
- it considers the importance of studying information on the conditions and environmental factors, as well as information about the events;
- it considers a long period of time, but it is based on previous studies of short (typical) time periods;
- it is structured (differentiated) according to several main lines of action, therefore, involves little detail.
- Strategic planning. The strategy cannot be a determination of the expected objectives and convenient methods for their achievement. The strategy should not arise from a dream but from the real possibilities of development of the territory. Therefore, the strategy is the reaction of governments to the objective external and internal factors of business environment. The main issue of strategic planning is what we need to accomplish? The strategic planning is the overall planning activities.
- Tactical planning. The term «strategy» is originally a military term of Greek origin, meaning maneuvering forces, suitable for the realization of the main goal. Tactical planning – decisions about how resources should be allocated for the territory of the main goal. Tactical planning usually covers the medium term, that is, the subject concerns the middle and lower managers. Tactical planning focuses on how public authorities, associations and local communities should have the desired state. The difference between strategic and tactical planning is the difference between means and ends. The tactical planning is an important detail (functional) planning.
- Operational planning. This concept is most clearly emphasizes that the plan is the main goal of economic transactions in the total flow in the limited period (for example, sales planning, marketing, monitoring, etc.). Under the operational planning we understand the preparation or adjustment of a short-term budget work in the development of sustainable tourism.
Planning is carried out according to the levels of spatial organization and branch structure of the territory of recreation and tourism.
- Strategic planning (the highest level, or the whole territory) is the determination of the main components of activity in the long term, the evaluation of trends in the environment and the likely behavior of all competitors.
- Tactical (medium industries and / or groups of objects) plans is the determination of the main components of activity in the medium term, interim targets towards the achievement of strategic goals and objectives. The plans should identify the ways of management of the horizontal division of labor within a single administrative level to implement the ideas identified in strategic planning.
- Operating (local level or specific objects / process operation) plans determine short-term goals to solve tactical problems and are implemented at the lower level of government that involves the full participation of all stakeholders. The performance standards, job descriptions and other parameters are part of the system, which directs the efforts to achieve the overall and main goals of sustainable tourism.
Strategic planning consists of several interrelated stages:
- the formulation of the main characteristics of planning: the purpose, objectives, expected results;
- the preparation of the plan: collecting, organizing and updating information, analysis, specification of the goals and objectives of planning, setting targets to individual companies and groups of workers, the definition of the main events;
- the adoption of a plan: documentation and approval;
- the implementation of the plan.
The management of territorial tourist systems of different levels (global, regional, national, sub-national, local) is focused on the future vision and foresight of development [4-6]. The effectiveness of strategic planning for sustainable tourism development depends on the principal (leading) criteria:
- completeness characterizes the records of events and situations that may affect the activities;
- accuracy involves the use of modern methods and means that ensure the accuracy of forecasts;
- clarity characterizes a simplicity and clarity in the formulation of goals and methods;
- continuity is determined by a permanent character of goal-setting, including those on the basis of verification, review, correct orientation of development;
- efficiency involves a comparison of the costs of planning benefits that it gives.
Conceptual bases of strategic planning in the management of sustainable tourism development determine the basic 10 characteristics:
- the definition of a tourism product (service) needs to clearly and unambiguously identify the main features or attractors that are most likely to be interested and to attract tourists;
- the inventory of resources to determine what is the possibility of accommodation, food, transportation, entertainment, education, information and other services to provide tourists;
- the market involves identifying the types of visitors or submarkets, which are most likely to respond to the tourist product (service) in the region, as well as asseing the extent of competition with other regions within and outside the country;
- establishing international contacts requires the identification of foreign target markets and areas from which a «typical» tourist begins preparations for the first visit to «new» destinations, and optimal provision of necessary and useful information;
- the organization of work requires the establishment of an effective administrative mechanism for the coordination of direct and indirect efforts to attract tourists;
- improving domestic resource aims to modernize the infrastructure that would be contributed to the fact that the first visitors who arrived immediately felt welcome; after his/her return they will encourage friends, relatives and colleagues on vacation in this destination;
- processing of information sources provides a rapid response to marketing efforts that will adapt future programs rest in varying patterns of travel, objectives and market conditions, recreation and tourism;
- the development of promotional materials requires the creation of a wide variety of print and electronic sources, which would be useful both for specialists involved in the planning of tourism, and tourists who choose the routes for travel;
- it provides for the involvement of experts to establish contacts with entities that have experience in the regions and countries where the operations are carried out, in order to increase efficiency of promotion of tourist products (services);
- the entry into a market is based on the careful selection and use of methods that allow to maximize the financial resources aimed at the promotion of tourist products (services) of the territory.
Principle (from the Latin. «principium» – initiation) – a belief, a point of view, a rule of conduct. For example, «It's against my principles», «a stupid principle», «argue about principles», «the principle of not going», etc. The principles of strategic planning in tourism – the basic principles (regulation), which built a scientific system and practice. The principles of strategic planning for sustainable tourism development include: focus; consistency; complexity; subordination (holism – the ratio of total and private); predestination (historicity); efficiency; the balance of interests; adaptability; variability; innovativeness; legitimacy (acceptance of authority); delegation; quality environment of life; ecological compatibility.
Procedure – 1) a long-term, consistent, orderly movement of things; 2) some of the complex standard actions. The term derived from the French procédure «procedure process» from the main word procéder «to act», from the Latin «procedure» – «go; move», and from the pro «forward, for, instead of», and «cedere» – «go», goes back to PraEuropean «ked» – «go, move». The Russian word «procedure» is borrowed from the German word «Prozedur» («Dictionary of Russian language with the inclusion of information about the origin of the Word», 2007). The procedure for strategic planning in tourism – an official procedure of actions, works, discussions and monitoring of results of the strategic planning process in tourism. It is divided into the following procedures: the definition of the mission; formulation of goals and objectives; analysis of the external environment; analysis of the internal environment (strengths and weaknesses); the choice of strategy (the main way to achieve the target); long-term planning (stages achievement); policy making (how to achieve the target); development of action (the structure of the goal); implementation of action (order of achievement); analysis, evaluation and monitoring of results.
Conclusions. The completed work allows to draw the following conclusions on the role of strategic planning in the management of sustainable tourism development: 1) the conceptual and normative foundations of strategic planning for sustainable tourism development are currently at the stage of final formation; 2) there is a large amount of material on the theory and methodology of strategic planning for the development of sustainable tourism, which are characterized by a variety of conceptual approaches to the solution of the main problem; 3) the principles and procedures of strategic planning – is a developing, but a very important part of management of sustainable tourism development.
















Reference lists